Job Wizard
Print Job Design and Execution.
The Job Wizard software allows
creating and editing the print jobs. Print jobs recorded to the database serve
as instructions for the spotter control software - Jobcontrol.
Start creating the print job with
a name that later will be used to start spotter to execute this job.
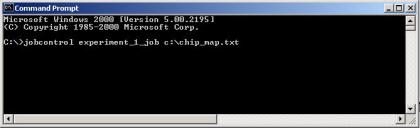
It is recommended to use
relatively short names for the print jobs, keeping in mind that it will be
necessary to input them form the keyboard in the Windows Command Prompt. The
job with the name shown at the screen shot above can be launched for execution
with the following string in the Command Prompt:
The Job Wizard prompts to save the
new name in the database before moving to the next screen in the wizard. Later
this name can be used for searching and editing the print job. Once an existing
job is edited it can be saved under the current name or under a new name at the
last step of the Job Wizard.
Step 2.
Microplate Specification
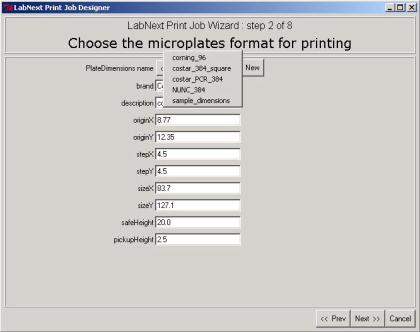
At the second step the Job Wizard
requires to specify parameters of the micro plate that will be used for
printing. Dimensions of micro plates of different vendors may vary
significantly. It is necessary to take measurements shown at the drawing below
or to find the dimensions using vendor's specifications.).
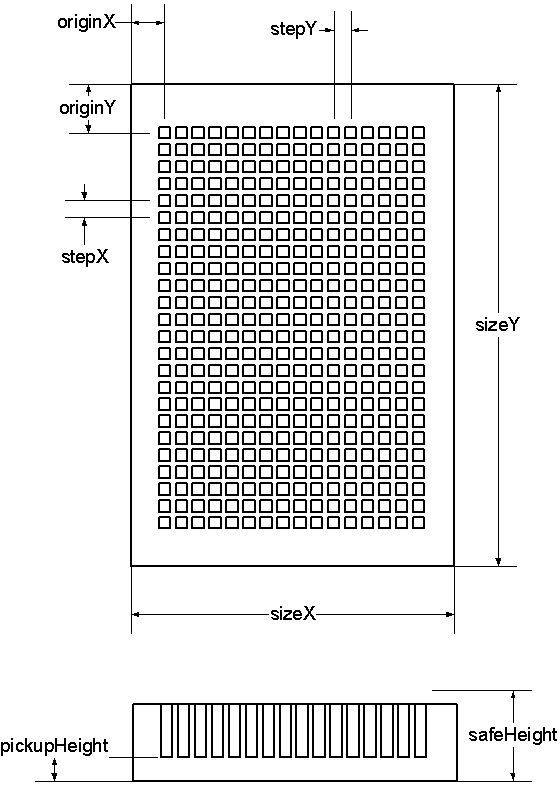
The measured parameters have to be
entered in the form at the step 2 of the Job Wizard and saved under a unique
name (COSTAR_384_PCR for example).
Once measured and registered the
micro plates can be used in the print jobs in the future by selecting the
relevant name. Their geometrical parameters will be automatically fetched from
the database.
Step 3. Registering Plates Content. Selecting Source Plates for the Microarray.
At this step positions of the DNA
clones in the source plates are being registered. Open the plate image form by
pressing the <New Plate Content> button. Pressing the <New Plate
Layout> button initializes a 384-wells plate with all wells empty. An empty
well must be marked by the "EMPTY" string and will be ignored by the
spotter. Any other string, even the blank one will be considered as a clone
name by the software and the corresponding well as containing a clone.
When printing with more than one
needle the spotter may sink needles in empty wells. Sometimes if the microplate
have been filled with a multi-channel instrument, some wells may contain only
the printing buffer with no DNA in it. Needles will be leaving spots on the
substrate surface with close to background intensity. These spots will not be
annotated.
It is makes sense to annotate
filled wells with the name of the clone in them.
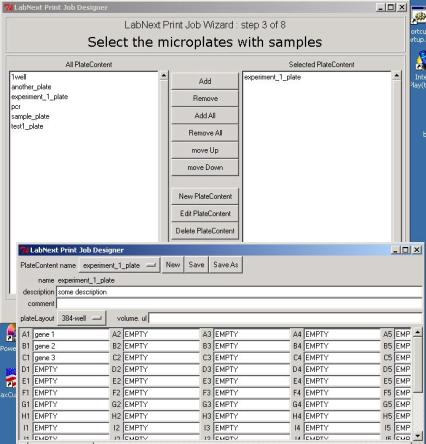
In order to select microplates
that will be used in this print job from the available microplates it is
necessary to mark them in the left panel "All Plate Content" and
pressing the <Add> button move them to the right panel "Selected
Plate Content". All DNA clones from the plates listed in the right panel
will be printed on the microarray. The <Remove> button excludes selected microplates
from the print job but not deletes them from the database. If there is more
than one microplate assigned for the print job the spotter will be stopping in
order to replace microplates that have printed with the new ones. The spotter
will print microplates in the same order they listed in the right panel
"Selected Plate Content". Pressing the <move Up>, <move
Down> buttons allows to change the order of microplates in the window and
therefore the printing sequence.
Step 4.
Printing Head Configuration.
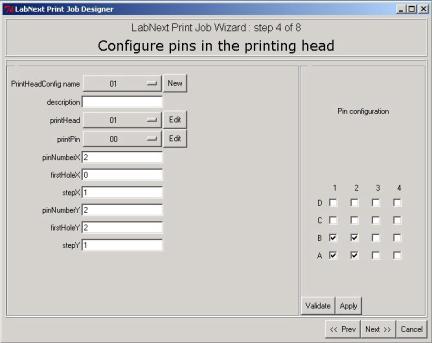
The configuration deals with
specifying head type, printing needles type and their positions in the head.
Although it is possible to edit geometrical specifications of printing heads
and needles form this program it is not recommended. There is a special program
named "Configure System" designed specifically for registering all
tools and configuring the system before the operations.
Each printing head configuration
can be saved under a unique name by pressing the button next to the "PrintHeadConfig name" label.
Similar buttons next to the "printHead" and "printPin"
labels open lists of heads and needles that have been registered already in the
database.
The number of needles and their
positions in the head can be edited in the right part of the "Pin
Configuration" window. On the 4x4 head pattern it is necessary to mark the
check boxes that correspond to the positions of needles in the real head. The
<Validate> button initiates configuration validity check. A number of
asymmetrical configurations not allowed and the system will generate the error
message in case eon of them has selected.
The <Apply> button registers
selected head configuration in the database. The numeric fields in the left
part of the window change their values according to the logic of selected
configuration.
Step 5.
Design of Microarray Pattern.
It is recommended to pay extra
attention to this step because positioning of spots on the chip strongly
affects quality of the following hybridization and scanning. It is an expedient
approach using one and the same microarray pattern for a logically linked
series of experiments. This can significantly improve data consistency.
Chip patterns can be saved in the
database under unique names and reused later for another microarrays. In order
to select a pattern that's already saved in the database it is necessary to
click the button next to the <Pattern> label. Patterns do not depend on
the DNA clones suppose to be printed on the microarray it is just a template to
deposit them.
The program allows designing
microarray pattern in the semi-automatic and manual modes. The semi-automatic
mode is the default one. The
<Advanced> button starts the manual mode.

In order to specify microarray
pattern it is necessary to fill out the fields in the "Desired
Pattern" panel. Please refer to the Print Geometry section of this manual
for additional information.
Number of Samples - not editable.
Shows the total number of clones form all plates assigned for printing in this
job.
Spots per sample - number of
repetitions for each clone. Duplicates of spots can be used for controlling
data repeatability in the experiment.
Arrays (zones) per slide - number
of identical arrays on one substrate. Arrays will be placed along the vertical
(long) side of the substrate.
Spot distance mm - spacing between
spots measured in millimeters.
Extra cluster distance mm -
distance between clusters OVER the minimal distance that keeps clusters from
overlapping.
Extra quad distance - distance
between quads OVER the minimal distance (that is equal to distance between the
needles)
The last two parameters limit
maximum allowed spots in the pattern. It makes sense to set them more that 0
only in case of the risk of spots merging during the printing of microarrays.
Enter 0 value in these fields to
let the program design the optimal pattern automatically. The pattern will be
created based on the following principles:
- The work surface of the
substrate logically divided into identical rectangular areas equal in number to
the number of zones (arrays) suppose to be printed on the substrate. Each array
will be printed in geometrical center of the corresponding zone.
- Each cluster of spots will be printed in 1xN pattern (as a
horizontal line).
- Extra quad distance will be set to maximum value that allows to
accommodate all required spots on the array.
Registering and Editing Parameters
of Substrates.
Clicking on the <Edit>
button right form the "Substrate" label opens the substrate
parameters window.
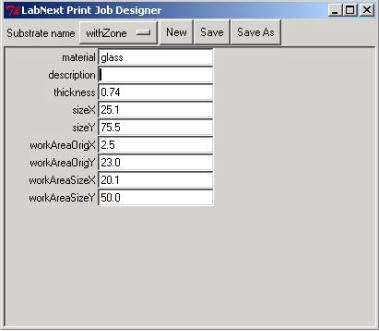
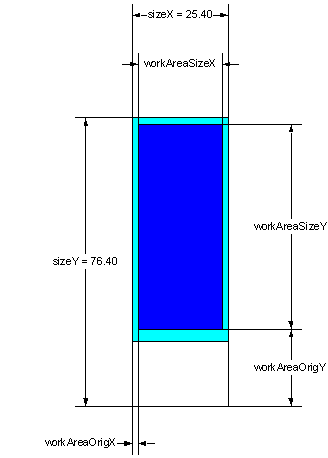
Meanings of the fields are:
- material - material that the substrate made out. (glass,
nylon, etc.)
- description - free format description. Non-mandatory field.
- thickness -
substrate thickness
The rest of parameters explained at the picture below.
It is possible to save parameters of substrates in the database and use them just selecting an appropriate name without editing the parameters before each printing.
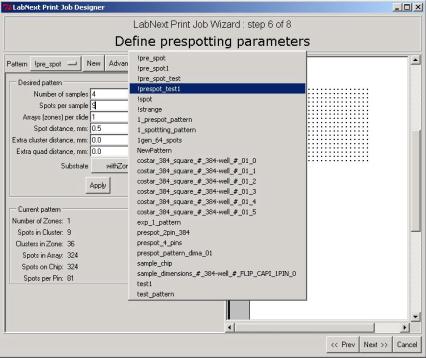
Step 6.
Design of Prespotting Pattern.
Prespotting is the deposition of a
number of spots on a separately assigned substrate (prespotting substrate) in
order to remove excessive liquid from tips of the needles right after samples
pick-up. Number of prespotting spots depends on the type of needles, material
of the substrate, viscosity of printing buffer and environmental conditions -
temperature and humidity. For the LabNEXT composite capillary needles this
number ranges from 1 to 6. In case of using a new printing buffer, other than
the LabNEXT printing buffer it is recommended to make a few test printing runs
in order to determine the number of prespotting spots require. Editing of
prespotting patterns is totally identical to editing the microarrays patterns.
Main criteria for designing of
prespotting patterns though differ form ones used for microarrays patterns. It
is recommended to by guided by the following principles:
- Use minimal possible number of
prespotting spots in order to save space on the prespotting substrates.
- It is possible to reduce the
distance between spots in comparison to the distance between sports in
microarrays and allow spots merging WITHIN ONE CLUSTER. A cluster consists of
spots with one and the same clone therefore there will not be risk of
contamination with adjacent clones.
- Clusters must not merge. To
prevent them from merging set the Extra Clusters Distance to a >0 value.
- Try to use fully the surface of
prespotting substrates.
- One and the same prespotting
layout can be used in many print jobs.
Step 7.
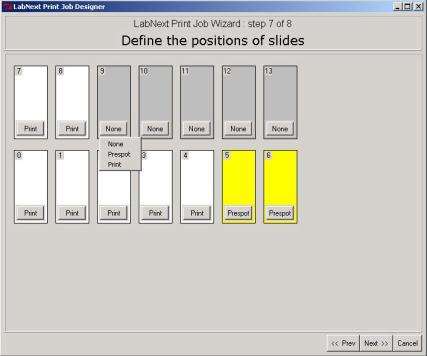
Placing Substrates on the Work Board of the Spotter.
Substrates can be placed in any
slide nests in any order. Press the button in the lover part of the image of a
slide nest to register positions of the glasses on the board. Register all
substrates in the way they are placed on the work board. The spotter prints
starting form the right lower substrate clockwise. It is better to put
prespotting substrates in the first positions on the printing path. Empty
positions will be ignored. If there are not enough prespotting substrates to
accommodate all prespotting spots the print run will be suspended and the
spotter control software will generate the message prompting to replace
prespotting spots.
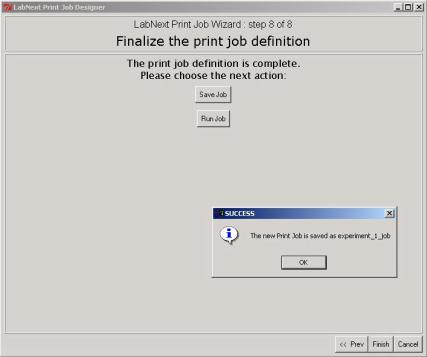
Clicking the <Save Job>
button can save print job. If there are unsaved changes the program will prompt
to save the job before finalizing the Job Wizard.
A print job launches from the
Windows Command Prompt that ca be found at StartàProgramsàAccessories.
Type in the Command Prompt window
the following string:
Jobcontrol [job name] [annotation
file path and name]
[job name] - name of a print job
you want to execute
[annotation file path and name] -
name of the file generated by the spotter that will be used by other
application for annotation of clones on the microarray images. There are no
limitations on the naming this file.