The horse radish peroxidase enzyme (HRP) is used in the DIAPOPS procedure to generate a color signal from a substrate
1. Introduction
The horse radish peroxidase enzyme (HRP) is used in the DIAPOPS procedure to generate a color signal from a substrate ![]() )
)![]() )
)
2. Data concerning horse radish peroxidase (HRP)
The following data concerning HRP is a summary of the material provided with the pure enzyme sold by Boehringer Mannheim(Peroxidase, horse radish, Lyophilized Grade I, Cat. No. 0121 606). This enzyme is used by DAKO A/S to prepare the streptavidin conjugated enzyme (DAKO, Streptavidin-HRP, Cat. No. P0397), which is used in the DIAPOPS procedure ![]() )
)
The data describes the unconjugated enzyme. No data have been found on the optimal conditions of the conjugated enzyme. Although it is to be expected that the conjugated enzyme may yield slightly different optimum conditions in practical experiments, no difference between the data given below and the performance of the streptavidin conjugated enzyme has been observed in the numerous DIAPOPS experiments conducted.
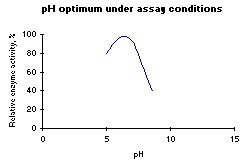 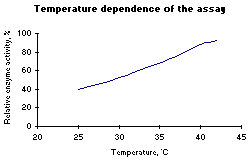 Figure 1: Left: pH optimum of HRP. Below: Temperature optimum of HRP. |
| Nomenclature: | donor : hydrogen-peroxide ixidoreductase, EC 1.11.1.7 |
| Molecular weight: | 40,000 |
| Isoelectric point: | 7.2 |
| Structure: | Glycoprotein with one mole of protoheme IX |
| Inhibitors: | Cyanide, sulfide, fluoride, azide, hydroxylamine, hydroxyl ions |
| Activators: | Peroxidation of o-dianisidine is accelerated by ammonia, pyridine, imidazole at pH values > 7.0 |
| pH optimum: | 6.0-6.5 (Figure 1 left) |
| Temperature dependence: | See Figure 1 right |
| pH stability: | 4.0 - 10.0 |
| Thermal stability: | Below 60ºC (Figure 2) |
| Specificity: | Peroxidase is specific to the hydrogen acceptor; only H2O2, methyl- and ethyl peroxides are active. In contrast, the enzyme is not specific for the hydrogen donor. A large number of phenols, aminophenols, diamines, indophenols, leuco dyes, ascorbate, and several amino acids react. |
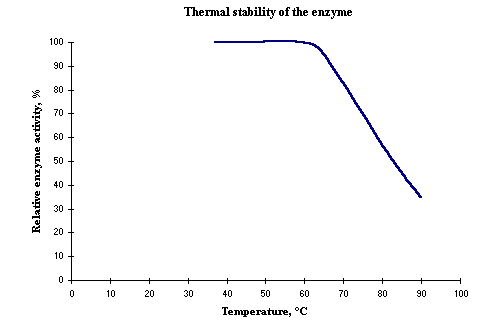 Figure 2: Thermal stability of the enzyme. |
3. Substrate
Only one substrate has been used in DIAPOPS with HRP: TMB. Other substrates, such as OPD, do not have the necessary sensitivity and have not been tested.
3 a). 3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB)
TMB is oxidized during the enzymatic degradation of H2O2 by horse radish peroxidase. The structure of TMB can be seen in Figure 3. The oxidized product of TMB has a deep blue color. A clear yellow color is formed after addition of the acidic stop solution ![]() )
)
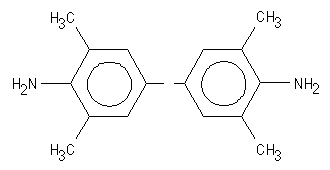 Figure 3: The structure of 3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB). |
4. A comparison between alkaline phosphatase and HRP in DIAPOPS
A comparison in a DIAPOPS assay was made between alkaline phosphatase (AP) ![]() )
)
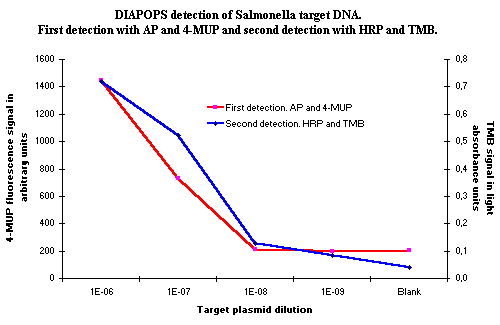 Figure 4: DIAPOPS results from a detection of Salmonella plasmid DNA. Two detections have been performed in the same NucleoLink Strips. The first detection was with AP and 4-MUP as substrate and the second detection was with HRP and TMB as substrate. As observed, TMB yields the best detection limit in this experiment, but the performance is approximately equal. |
5. Conclusion
HRP is an enzyme which may yield a good performance in the DIAPOPS procedure. However, there are only a few substrates available with the sensitivity demanded to detect the samples with low template concentrations in DIAPOPS. TMB is a very sensitive substrate for DIAPOPS, and may yield results as good as those obtained with alkaline phosphatase using 4-MUP as the substrate ![]() )
)
The problem of using HRP in DIAPOPS is the addition of acid to stop the enzymatic reaction. This addition of acid cleaves the covalently bound solid phase product from the wells, and rehybridization ![]() )
)