In DIAPOPS
1. Introduction
In DIAPOPS ![]() )
)![]() )
)![]() )
)
2. EDC
1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide (EDC) is a water-soluble derivative of carbodiimide. Carbodiimide catalyzes the formation of amide bonds between carboxylic acids or phosphates and amines by activating carboxyl or phosphate to form an O-urea derivative. This derivative reacts readily with nucleophiles. The reagent can be used to make ether links from alcohol groups and ester links from acid and alcohols or phenols, and peptide bonds from acid and amines (Tedder et al. 1972). Carbodiimide is often used in the synthesis of peptides as the water-soluble derivative EDC or as the organic soluble derivative, N,N'-dicyclohexyl-carbodiimide (DCC).
3. Activation of the 5'-end phosphate group with carbodiimide
The first step in the binding reaction is an EDC activation of the 5'-phosphate group on the solid phase primer (or a phosphoryl group on any DNA, single- or double-stranded). This is shown in Figure 1. It is very likely that other groups, such as amines, could be used as coupling groups in the 5'-end with the same efficiency as the phosphate group, but it has not been tested. However, experiments have demonstrated that without a phosphate group there is no binding of primers to the NucleoLink surface which can be used in the solid phase amplification. For this reason it is very important to phosphorylate the 5'-end.
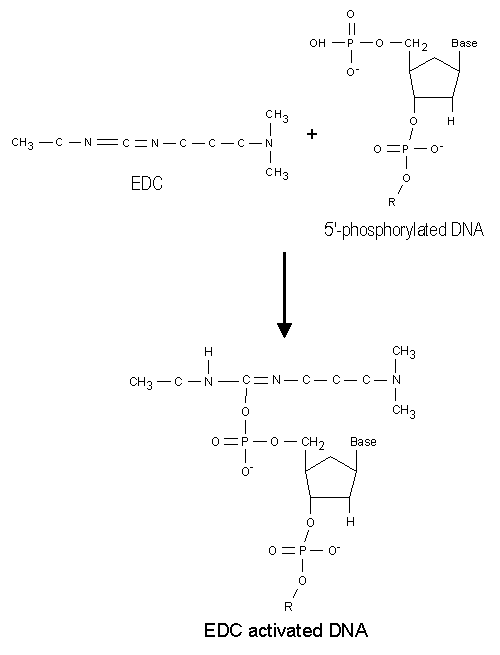 Figure 1: The 5'-end phosphorylated DNA is activated in a reaction between the phosphate group and EDC. |
4. Reaction of the carbodiimide activated DNA with 1-methylimidazole
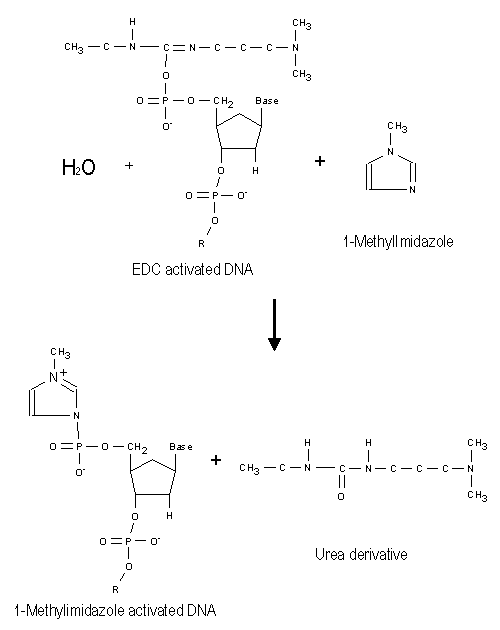 Figure 2: The reaction between the EDC-activated phosphate group in the 5'-end of the DNA and 1-methylimidazole to form a more stable compound. |
The EDC activation of DNA readily occurs in aquaeous solutions, and the activated DNA may react with the surface of NucleoLink. However, the half-life of EDC activated DNA is very short in water, and further conversion with 1-methylimidazole is therefore utilized. 1-Methylimidazole reacts with the EDC activated DNA and forms another active group, which is more stable in aqueous solution. This is illustrated in Figure 2.
1-Methylimidazole is a very efficient leaving group after attachment to the phosphate group on the 5'-end of the DNA and experiments for optimization of the coupling reaction have yielded very good results with this reagent (Rasmussen et al. 1991).
5. Binding to the surface
A reactive group on the NucleoLink surface reacts with the 1-methylimidazole activated DNA to form a covalent bond between the surface and the DNA. This is shown in Figure 3. This bond is thermostable ![]() )
)
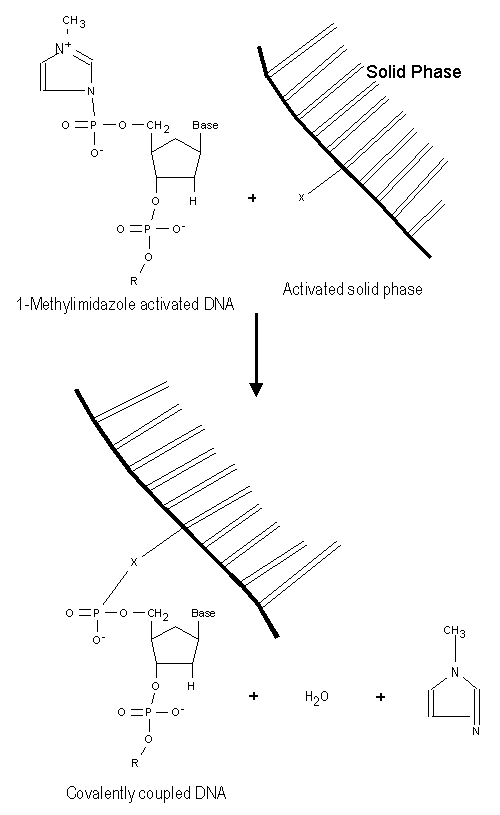 Figure 3: The reactive group on the NucleoLink surface indicated with an X, reacts with the phosphate group on the DNA coupled to 1-methylimidazole, and the covalent binding is created. Water and 1-methylimidazole are by-products of the reaction. |
6. Half-life of activated DNA
The use of 1-methylimidazole permits the compounds to be mixed in advance. If EDC and DNA were mixed in pure water, the activated DNA, which is the product of the reaction illustrated in Figure 1, would react quickly with water and hydrolyze (results not shown). DNA activated with 1-methylimidazole is more stable, and the single reagents can therefore be mixed in advance, without loss of coupling efficiency ![]() )
)
7. Conclusion
EDC is the active condensing reagent in the covalent binding of the solid phase primer to the surface of the NucleoLink Strips. The phosphate group in the 5'-end of the DNA is activated with EDC. 1-Methylimidazole is used to stabilize the activated DNA.