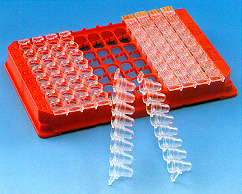
 Figure 1: NucleoLink™ Strips and Frame |
Product Information on NucleoLink™ Strips
Welcome to this introductory text describing the NucleoLink™ Strips from Nunc A/S. The NucleoLink Strips are presented in Figure 1 ![]() )
)![]() )
)![]() )
)
2. Product Information on NucleoLink™ Strips
| Format | ||||
| Which format does NucleoLink™ have? | NucleoLink™ consists of thin walled 8-well strips for assembly in a frame which is of 96 MicroWell® format. | |||
| Application | ||||
| What are the main applications of NucleoLink™ Strips? | The thin walled NucleoLink™ Strips are optimized for Solid Phase Amplification. By using the NucleoLink™ Strips conventional and time consuming methods such as Gel Electrophoresis and Southern Blotting are replaced by a much faster »ELISA-like« procedure: DIAPOPS (Detection of Immobilized Amplified Product in a One Phase System) | |||
| How easy is it to use NucleoLink™? | It is very easy, as there is no need to transport the amplicon to a second vessel for detection after amplification. The possibility to use »ELISA-like« procedures (eg ELISA conjugates, substrates and instruments) for the detection as an alternative to radioactivity makes it convenient and safe to use. | |||
| NucleoLink™ versus CovaLink™ | ||||
| What is the main difference between NucleoLink™ & CovaLink™? | The NucleoLink™ product provides a more heat stable surface than the CovaLink™ when used for nucleic acid (DNA and RNA) assays, while maintaining the covalent high binding capacity. | |||
| For which applications will NucleoLink™ substitute CovaLink™? | For DNA and RNA applications. CovaLink™ could be preferred in some hybridization assays where a higher working volume is desired. CovaLink™ Modules may also be used in some solid phase PCR assays, or other assays requiring a solely 5' coupling of the nucleic acid to the surface. | |||
| What are the main advantages of NucleoLink™? | NucleoLink™ Strips are optimized for solid phase amplification (thin walls | |||
| Features | ||||
| What is the recommended working volume for NucleoLink™? |
| |||
| Which material is NucleoLink™ made of? | An activated heat stable polymer formulated by Nunc. | |||
| How are the strips sealed? | Tape sealed - using Tape 8. | |||
| Can the strips be autoclaved? | When using NucleoLink™ Strips it is not necessary to autoclave. | |||
| Which temperatures are the strips resistant to? | From -20 to 120ºC | |||
| Binding | ||||
| Which kind of molecules do the NucleoLink™ bind? | Nucleic acids. | |||
| How are the nucleic acids bound to the wells? | Covalently via carbodiimide condensation. | |||
| Is it possible to store oligonucleotides covalently bound to a solidphase? | Oligonucleotides covalently bound to a solid phase can be used after prolonged storage at 4ºC. | |||
| DIAPOPS | ||||
| What is the DIAPOPS technique? | DIAPOPS (Detection of Immobilized Amplified Product in a One Phase System) is a technique where the same well is used for both amplification by solid phase PCR and subsequent detection by hybridization. Manipulation is simplified and contamination diminished since the transfer of amplicon from the amplification system to the detection system is eliminated. | |||
| What can DIAPOPS be used for? | DIAPOPS can be incorporated into a variety of screening and diagnostic probe assays, utilizing nucleic acid molecules for hybridization, amplification and detection. | |||
| Can DIAPOPS be used for quantitative analysis? | Yes. Using the DIAPOPS procedure a linear relationship between fluorescence signals and template is obtained for more than four logs of template concentrations. | |||
| How long does it take to perform the DIAPOPS assay? | Less than 3 hours with precoated strips (strips with one of the primers bound) | |||
| What is the detection limit? | 10-100 molecules per well. | |||
| Detection systems | ||||
| Which kind of detection methods have previously been used? | Colorimetric, fluorescent and radioactive. | |||
| Instrumentation | ||||
| Which thermocyclers are compatible with NucleoLink™? | Perkin Elmer 9600, MJ Research PTC 200. Techne Gene E and Hybaid OmniGene. | |||
| Can standard MicroWell® plate reader's be used? | NucleoLink™ can be used in MicroWell® format readers. | |||
| Can a multichannel pipette be used? | NucleoLink™ can be handled by equipment and multichannel pipettes designed for MicroWell® format. | |||
| Reduced risk of contamination | ||||
| Is there a risk of contamination between the wells? | No, negative and positive samples can be run in adjoining wells without cross contamination. | |||
| Is the contamination risk in the laboratory reduced when using NucleoLink™? | Yes, the risk of contamination is diminished since the transfer of amplicon from the amplification system to the detection system is eliminated. | |||
| Quality Control | ||||
| How is the quality of NucleoLink™ controlled? | Nunc certifies the PCR performance of the NucleoLink™ Strips. Every sleeve of Strips contains our certificate of performance. The DIAPOPS technique is used as a quality test of the performance of NucleoLink™. | |||
3. Handling NucleoLink™ Strips using the DIAPOPS technique
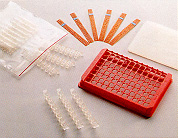 1. NucleoLink Strips, Tape 8, Spacer plate and Frame. 1. NucleoLink Strips, Tape 8, Spacer plate and Frame. |
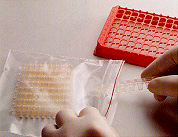 2. Packed in a zip bag, The NucleoLink Strips can be assembled in the required number. 2. Packed in a zip bag, The NucleoLink Strips can be assembled in the required number. |
 3. The NucleoLink™ Strips are inserted in a standard MicroWell® frame for easy handling. 3. The NucleoLink™ Strips are inserted in a standard MicroWell® frame for easy handling. |
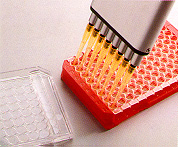 4. Phosphorylated primer and carbodiimide solution are added to all wells. 4. Phosphorylated primer and carbodiimide solution are added to all wells. |
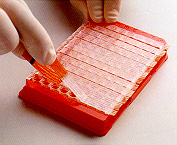 5. The wells are sealed with tape to avoid evaporation. 5. The wells are sealed with tape to avoid evaporation. |
 6. The primer is covalently attached to the well during five hours of incubation at 50ºC. 6. The primer is covalently attached to the well during five hours of incubation at 50ºC. |
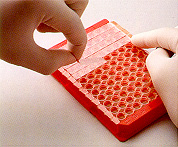 7. The tape is removed after incubation. 7. The tape is removed after incubation. |
 8. The wells are washed to remove non-bound primer. 8. The wells are washed to remove non-bound primer. |
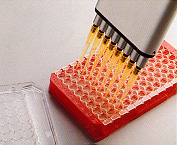 9. PCR solution (dNTP, primers, Taq, template) is added to all wells. 9. PCR solution (dNTP, primers, Taq, template) is added to all wells. |
 10. The wells are sealed with tape to avoid evaporation during the PCR process. 10. The wells are sealed with tape to avoid evaporation during the PCR process. |
 11. The NucleoLink™ Strips are mounted in the thermocycler. 11. The NucleoLink™ Strips are mounted in the thermocycler. |
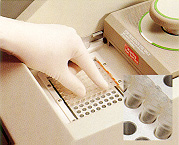 12. The NucleoLink™ Strips fit perfectly in 0.2 ml blocks. 12. The NucleoLink™ Strips fit perfectly in 0.2 ml blocks. |
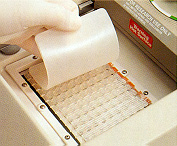 13. The spacer plate is placed on top of the NucleoLink™ Strips. 13. The spacer plate is placed on top of the NucleoLink™ Strips. |
 14. The lid of the thermocycler gives a uniform pressure to all the NucleoLink™ Strips. 14. The lid of the thermocycler gives a uniform pressure to all the NucleoLink™ Strips. |
 15. The NucleoLink™ Strips are released from the heating block by using standard angle pincers. 15. The NucleoLink™ Strips are released from the heating block by using standard angle pincers. |
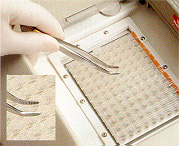 16. View of push out tool (angle pincers). 16. View of push out tool (angle pincers). |
 17. The NucleoLink™ Strips are removed from the thermocycler and mounted in the frame. 17. The NucleoLink™ Strips are removed from the thermocycler and mounted in the frame. |
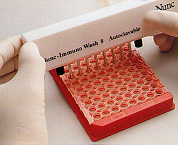 18. Non covalently immobilised amplicons and PCR reagents are removed by washing. 18. Non covalently immobilised amplicons and PCR reagents are removed by washing. |
 19. The biotinylated detection probe is added to all wells. 19. The biotinylated detection probe is added to all wells. |
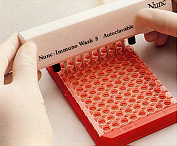 20. The wells are washed after incubation. 20. The wells are washed after incubation. |
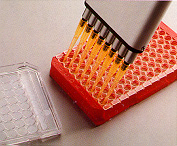 21. Alkaline phosphatase labelled streptavidine is added to all wells. 21. Alkaline phosphatase labelled streptavidine is added to all wells. |
 22. The wells are washed after incubation to remove non-bound labelled streptavidine. 22. The wells are washed after incubation to remove non-bound labelled streptavidine. |
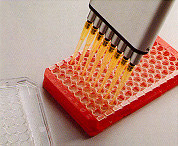 23. Fluorescent substrate (4-MUP) is added to all wells. 23. Fluorescent substrate (4-MUP) is added to all wells. |
 24. The wells are read in a fluorometer after incubation. 24. The wells are read in a fluorometer after incubation. |
 25. Final result and data reduction. 25. Final result and data reduction. |
| Cat. No. | Description | Units per Sleeve/Carton/Case | Material |
| 248259 | NucleoLink™ Strips | 12/120/1440 | Activated heat stable Polymer |
| 249182 | Frame | 6/72 | Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) |
| 250105 | Tape 8 and Spacer Plate | 60/480/5760 1/12 | Polyester Silicone Rubber |
| 249719 | Tape 8 | 60/480/5760 | Polyester |
| 249344 | NucleoLink™ Starter Kit | 1/12 48 NucleoLink™ Strips, 1 Frame, 60 Tape 8, 1 Spacer Plate and Application Litterature/kit | |
*The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) process is covered by US patents owned by Hoffmann-La Roche, Inc and F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.